Source: Finally Master Next.js’s Most Complex Feature - Caching (webdevsimplified.com)
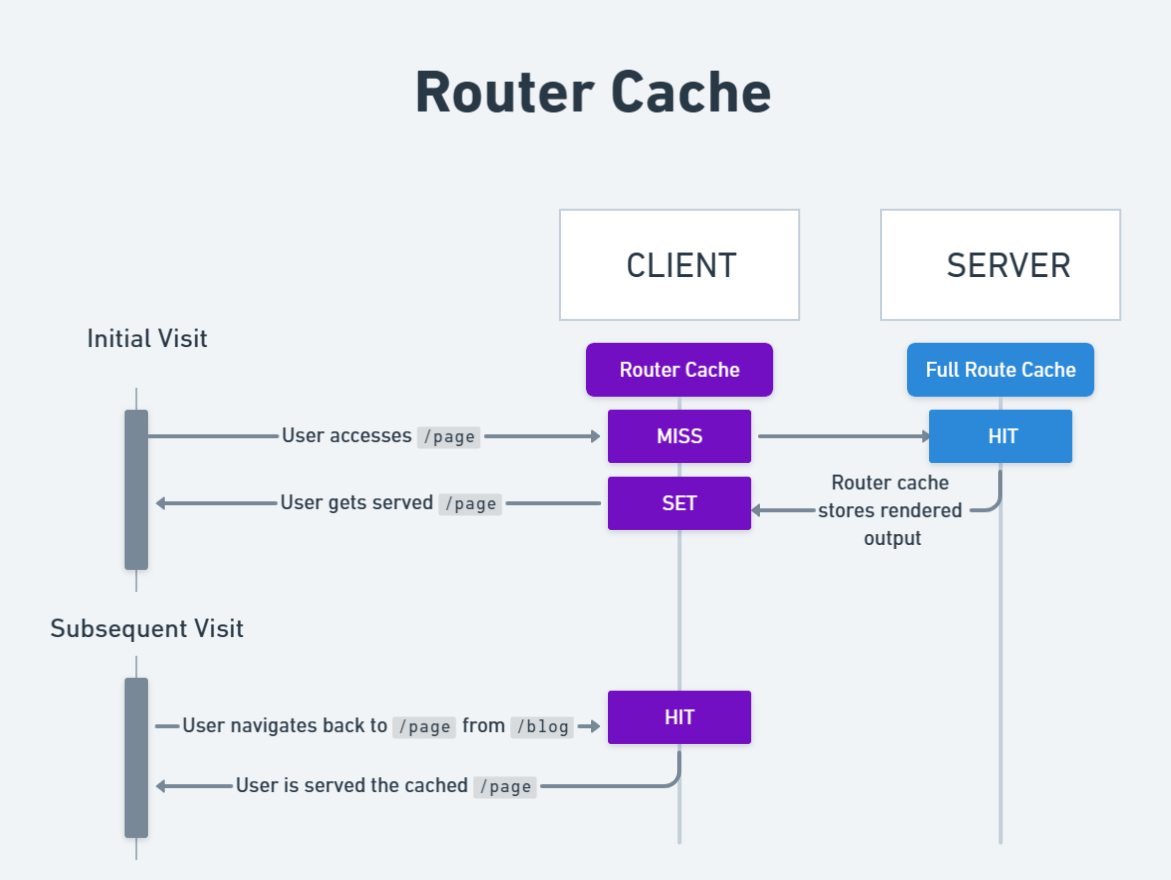
Before we learn about the router cache, we should know that the Full Route Cache stores both HTML and RSCP persistently on the server over multiple user requests.
The router cache, on the other hand, only caches RSCP in the client browser for the duration of a user session. Furthermore, while the Full Route Cache caches only statically rendered routes, the router cache caches both statically and dynamically rendered routes.
The duration of the stored cache depends on the route type:
- Static route: the cache is stored for 5 minutes.
- Dynamic route: the cache is stored for 30 seconds.
export default async function Page() {
const blogData = await getBlogList()
return (
<div>
<h1>Blog Posts</h1>
<ul>
{blogData.map(post => (
<li key={post.slug}>
<Link href={`/blog/${post.slug}`}>
<a>{post.title}</a>
</Link>
<p>{post.excerpt}</p>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
)
}For example, when the user navigates to this static page, the RSCP of this page gets stored in the router cache for 5 minutes. Subsequently, if the user navigates to a dynamic blog post page, namely /blog/${post.slug}, the RSCP of that page will also get cached in the router cache, but for 30 seconds.
Revalidation
- When the user closes the tab or refreshes the page, the cache is cleared.
- Using
revalidatePath,revalidateTag, orrouter.refreshwill clear the cache.
References